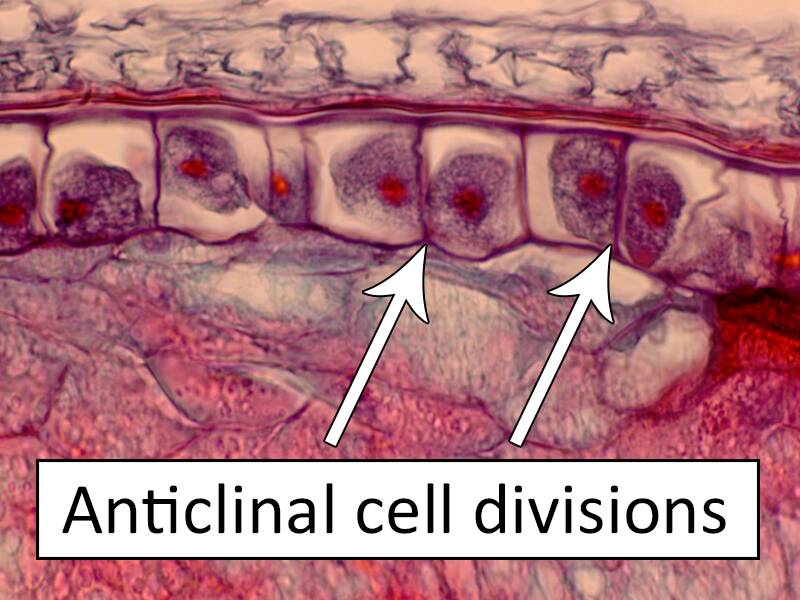
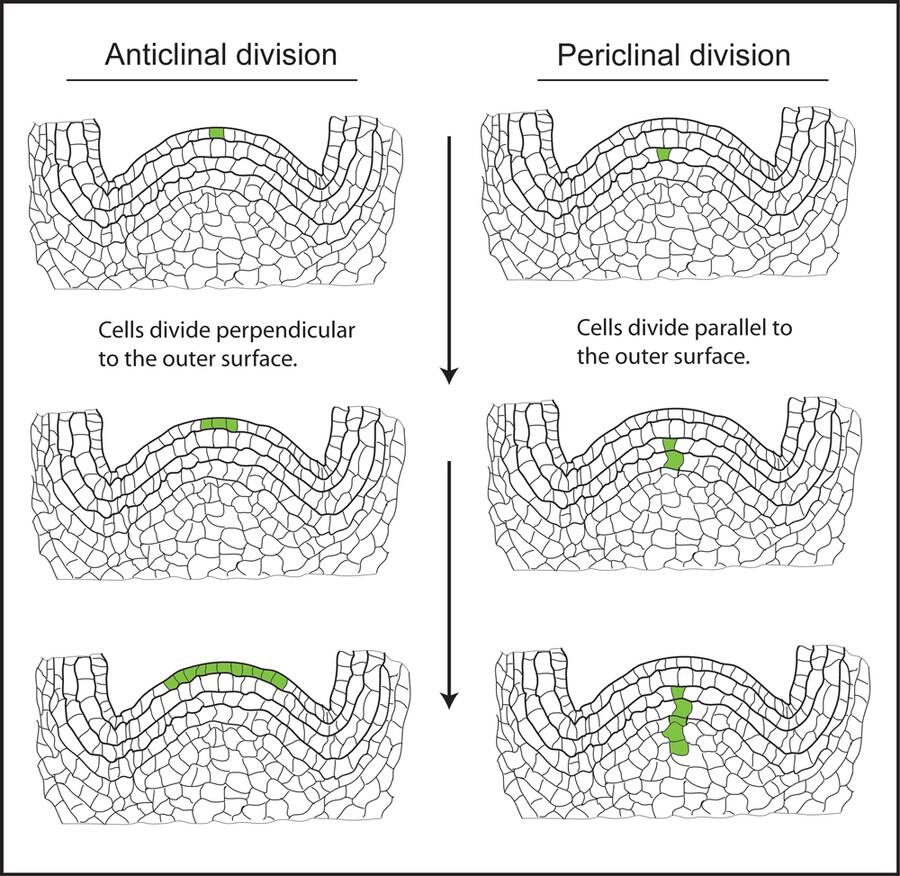
The epidermis is a very specialized cell layer characterized by anticlinal cell divisions.
A thick cuticle and wax coverings help to reduce water loss.
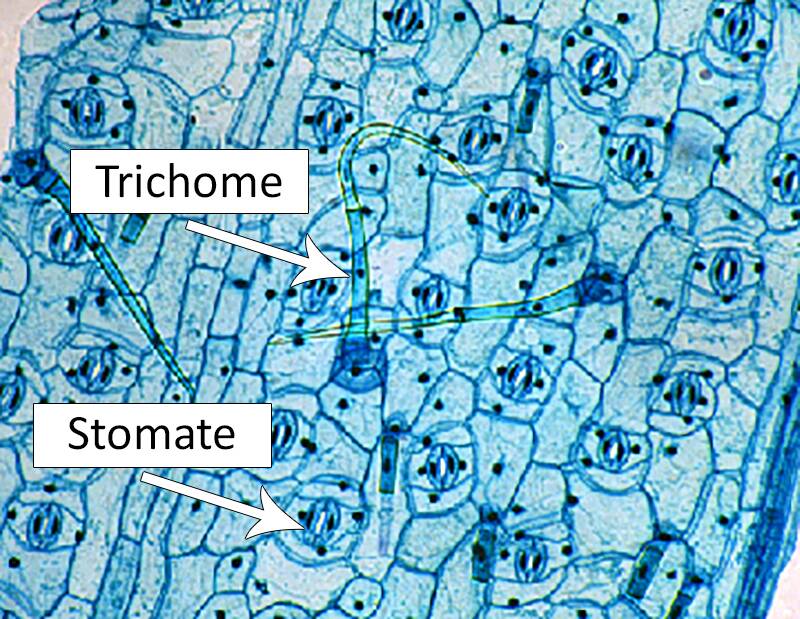
Specialized epidermal cells include trichomes and stomata.
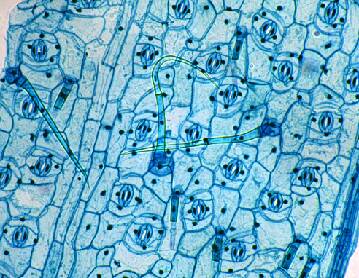
Cuticle - The outer waxy covering on the epidermis of stems, leaves, and fruit.
The cuticle protects the epidermal surface from drying out. Plants native to arid climates can have extremely thick cuticles.
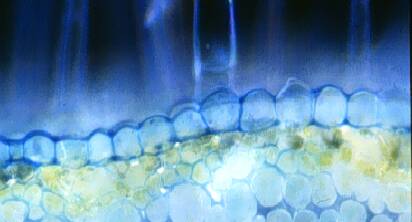
Note anticlinal cell divisions and cuticle on surface of cells.
Anticlinal cell division is the plane of division perpendicular to the surface of the organ.
This is in contrast to periclinal cell divisions that are parallel to the outer surface.
The epidermis is not a homogeneous group of cells.
A leaf surface can also contain trichomes and stomata.