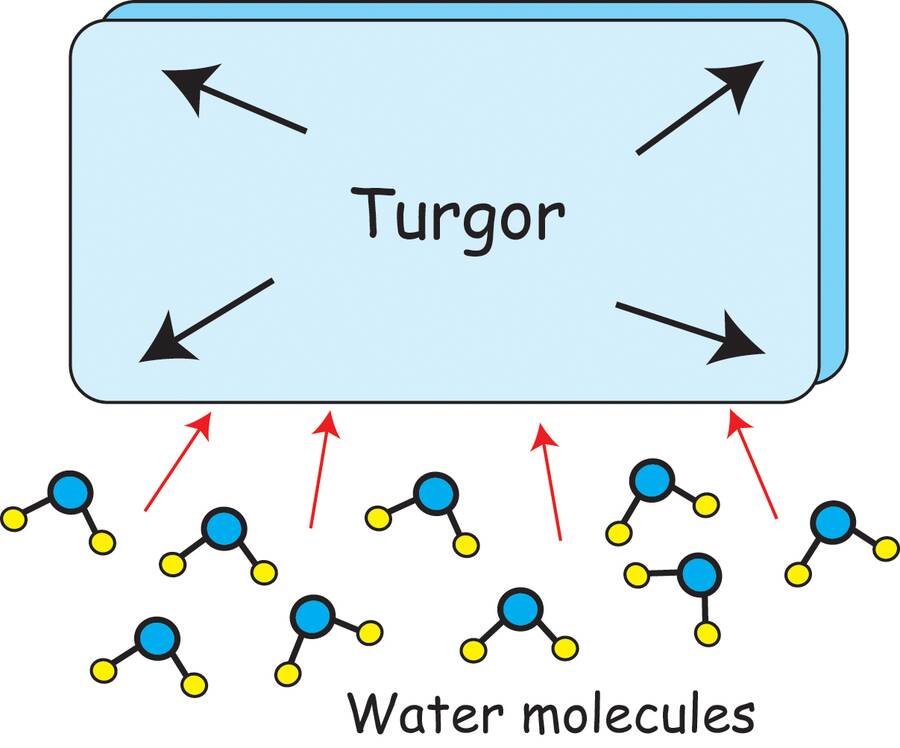
Turgor is maintained by the water inside the cell.
Water moves into or out of the cell by osmosis and is based on the water potential of the cell.
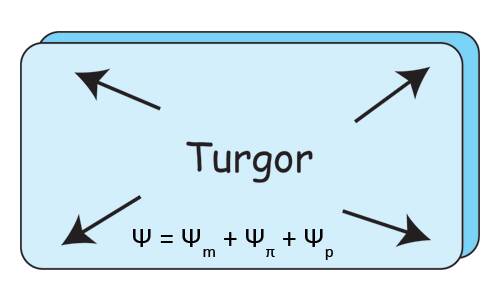
The cell's water potential is equal to the sum of the : Ψ = Ψm + Ψπ + Ψp
Matric potential Ψm
Osmotic potential Ψπ
Pressure or turgor potential Ψp
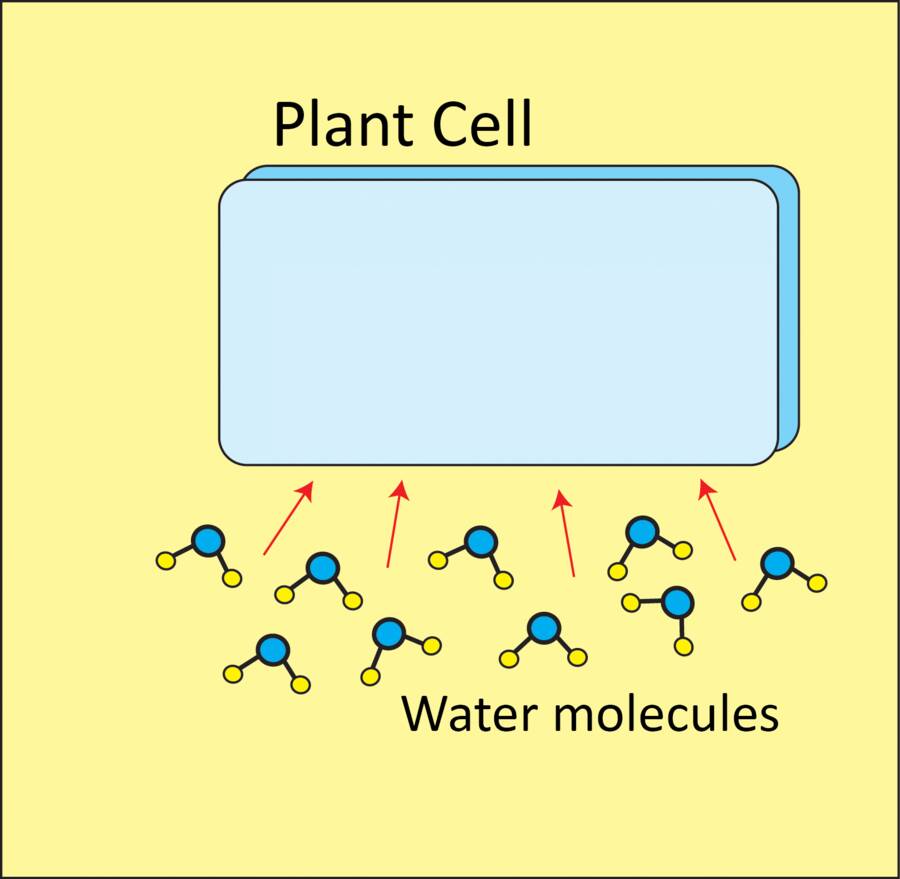
A major way that the cell remains turgid is by keeping a negative osmotic potential in the vacuole where the cell stores sugars, amino acids and organic acids.

Water moves into or out of the cell due to osmosis.
Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane in response to the osmotic potential on either side of the membrane.
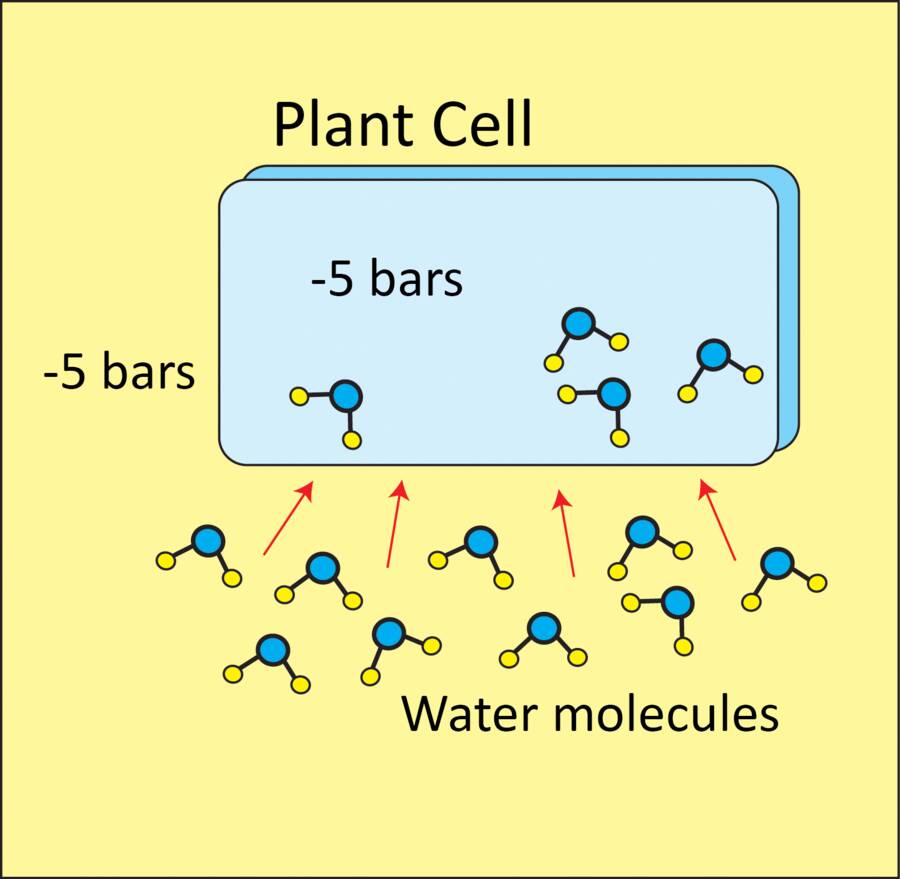
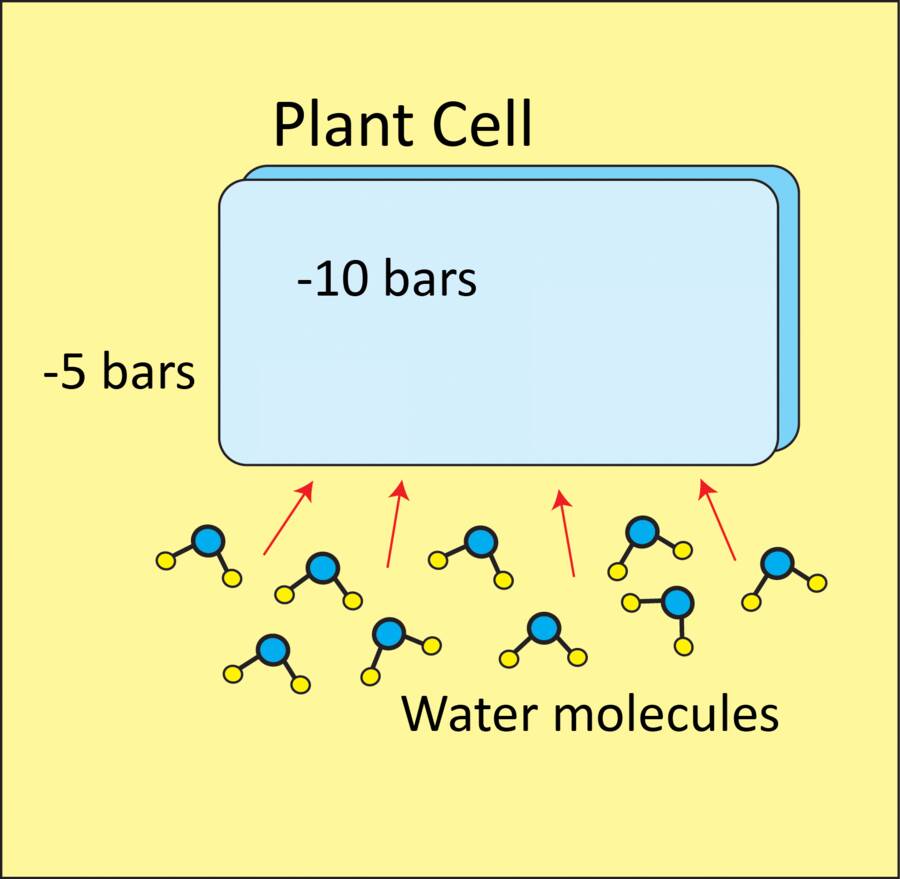
Water moves to areas with more negative osmotic potential. Osmotic potential is measured in bars or megaPascals.
In this example, water will move into the cell because it has the more negative osmotic potential.
Water no longer moves into the cell when the water potential inside and outside are at equilibrium (-5 bars).