The tetrazolium test is a biochemical method in which viability is determined by the red color appearing when cut seeds or isolated embryos are soaked in 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
Living tissue changes the tetrazolium to an insoluble red compound called formazan. The test is positive for dehydrogenase enzymes in respiration.
Seeds are treated with a 0.1 to 1.0% solution usually for 24 hours.
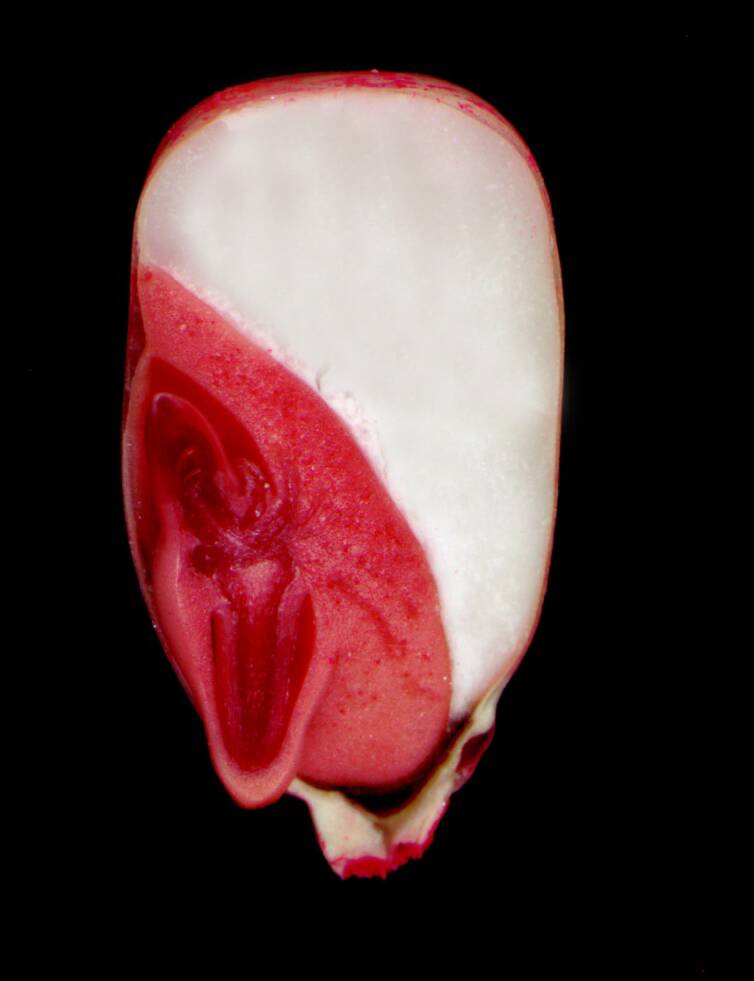
The seed lot here was treated with tetrazolium. It shows bright red embryos that are viable, pink embryos that are rapidly loosing viability and non-viable embryos that do not stain and are white.



