A rhizome is a specialized stem structure in which the main axis of the plant grows horizontally at or just below the ground.
Most species that make rhizomes are monocots, but there are a few examples in dicots and ferns produce rhizomes or rhizome-like structures.
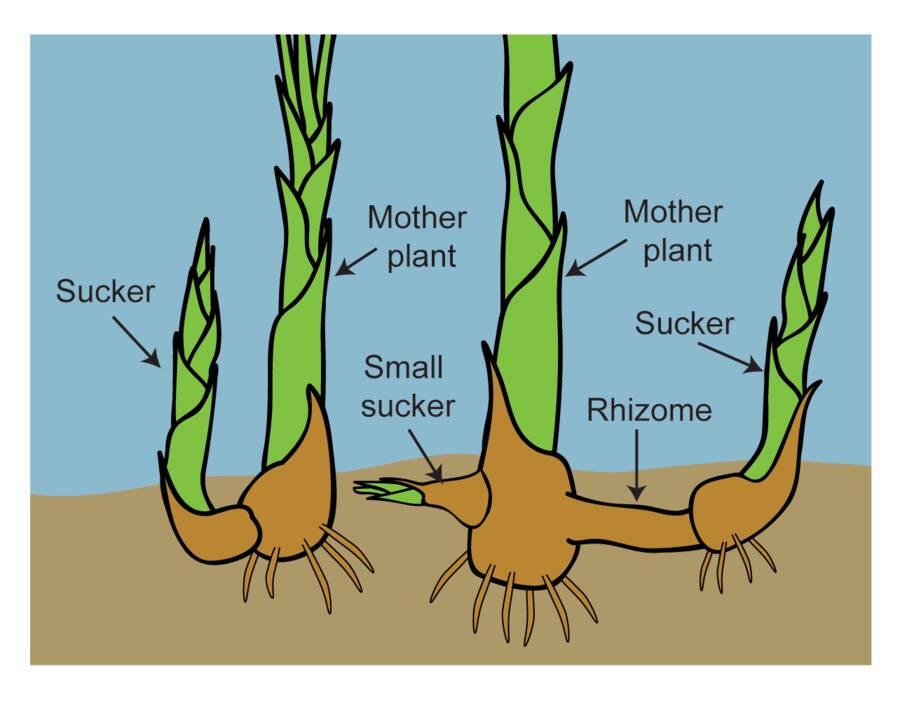
There are two main types of rhizomes:
- Leptomorphs
- Pachymorphs
Leptomorphs produce indeterminate stems that continue to develop new plants at each node.
Pachymorphs produce large slow growing horizontal stems that are determinate ending in a flowering stem.
There are also intermediate forms between the two called mesomorphs.

Leptomorph stems tend to have long internodes and have lateral buds at each node that may remain dormant or produce new shoots.
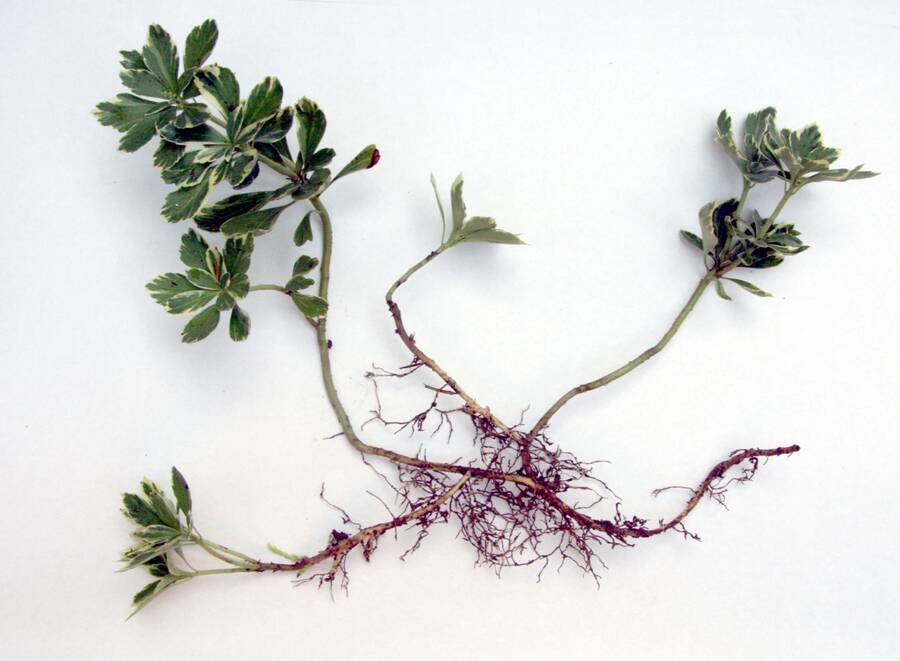

Pachysandra
Leadwort (Ceratostigma plumbaginoides) makes an excellent ground cover because it freely creeps by leptomorphic rhizomes.

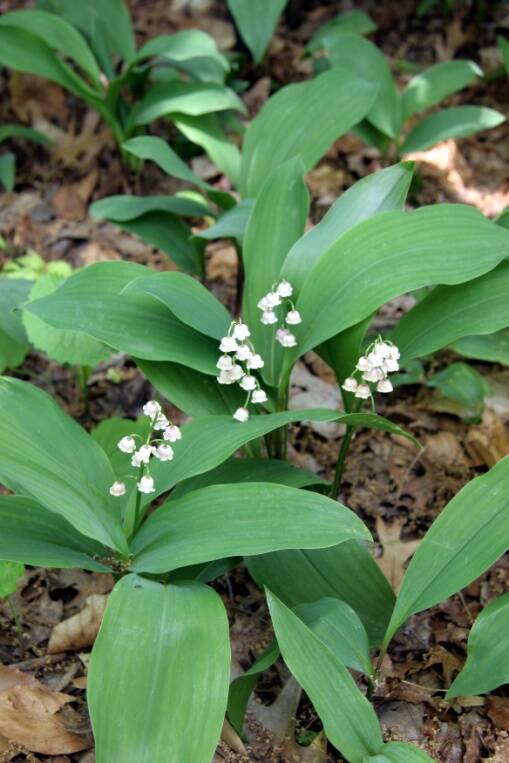
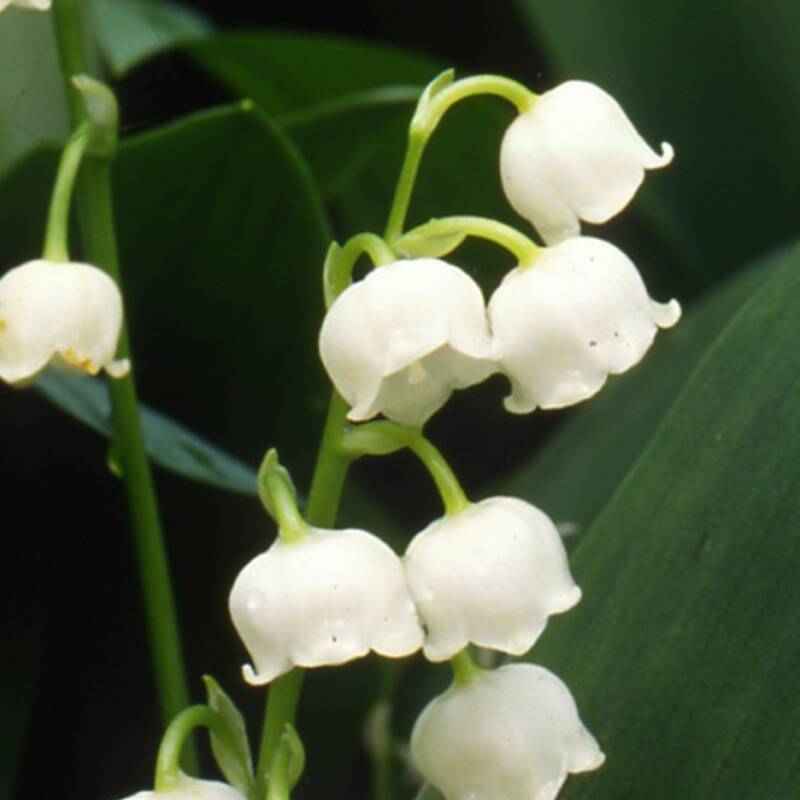
Leptomorphs do not form clumps, rather they spread extensively over an area as seen in plants like lily-of-the-valley (Convallaria).


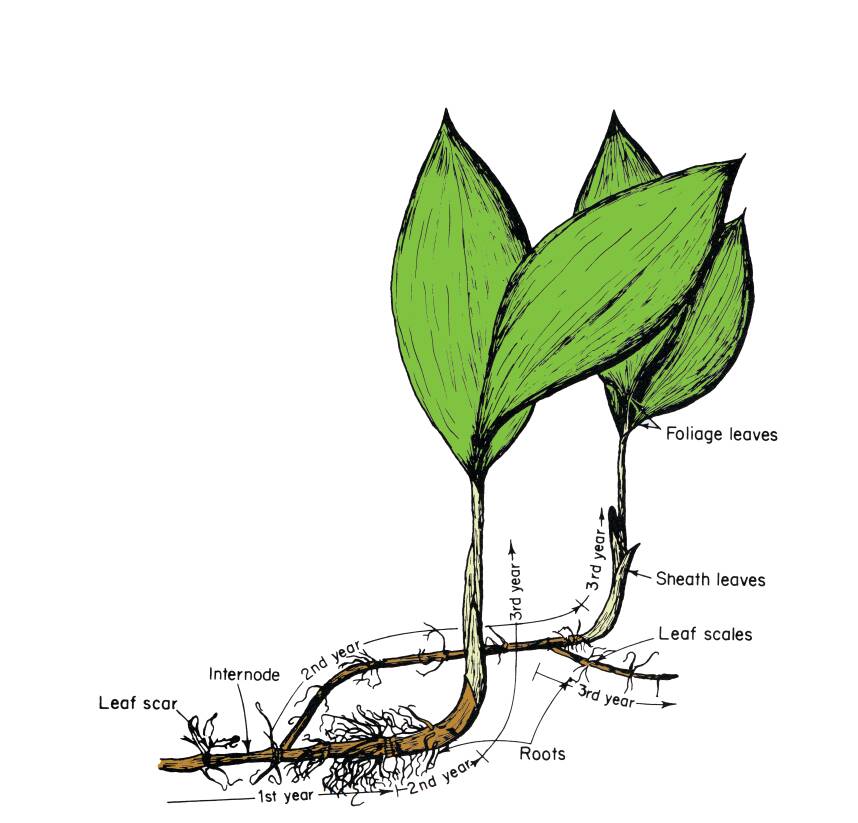
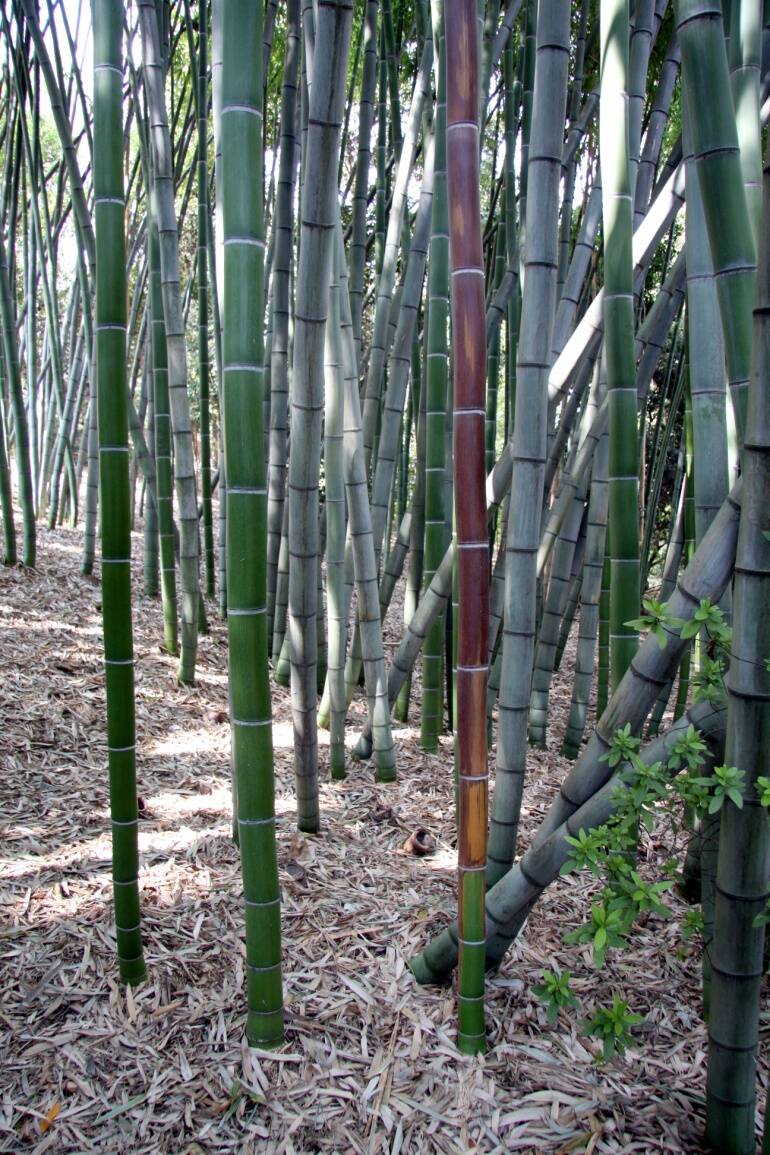
Bamboo can produce aggressive leptomorphic rhizomes that can spread over extensive areas.
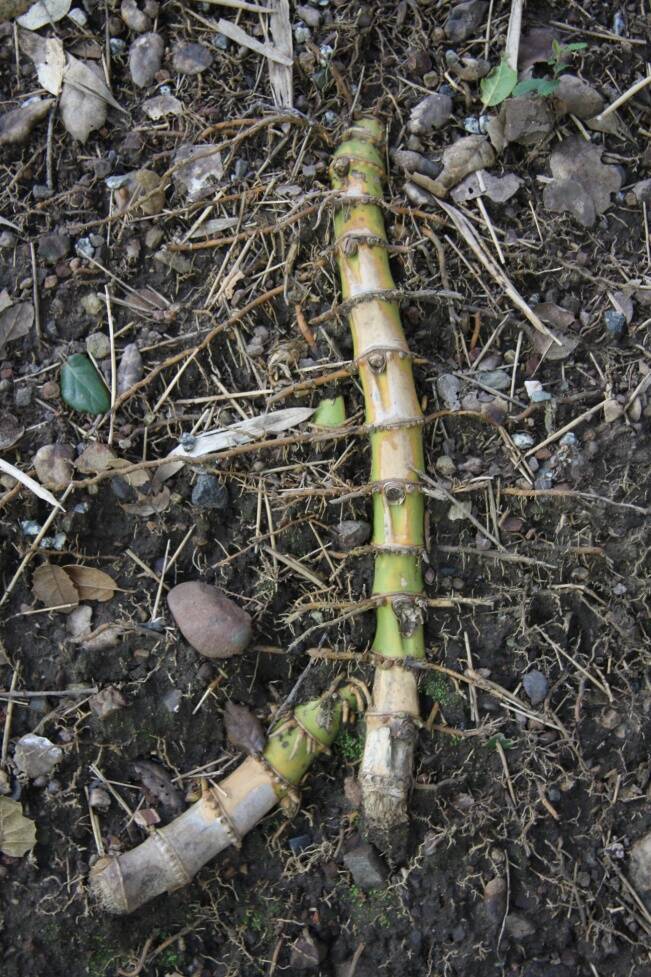


In contrast to a leptomorph, pachymorph rhizomes are determinant structures that terminate each season's growth with a flowering bud (arrow), while vegetative growth continues at the lateral buds.
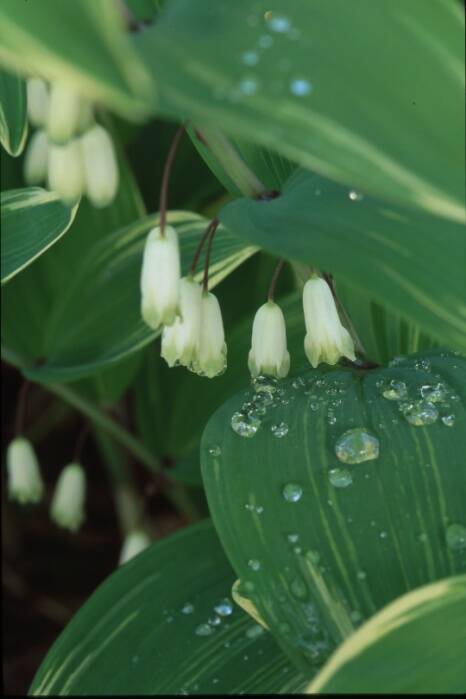

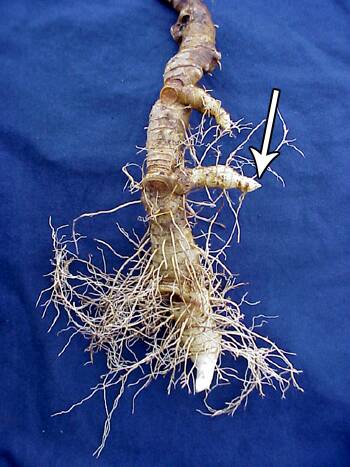
Trillium also develops from a pachymorph rhizome.
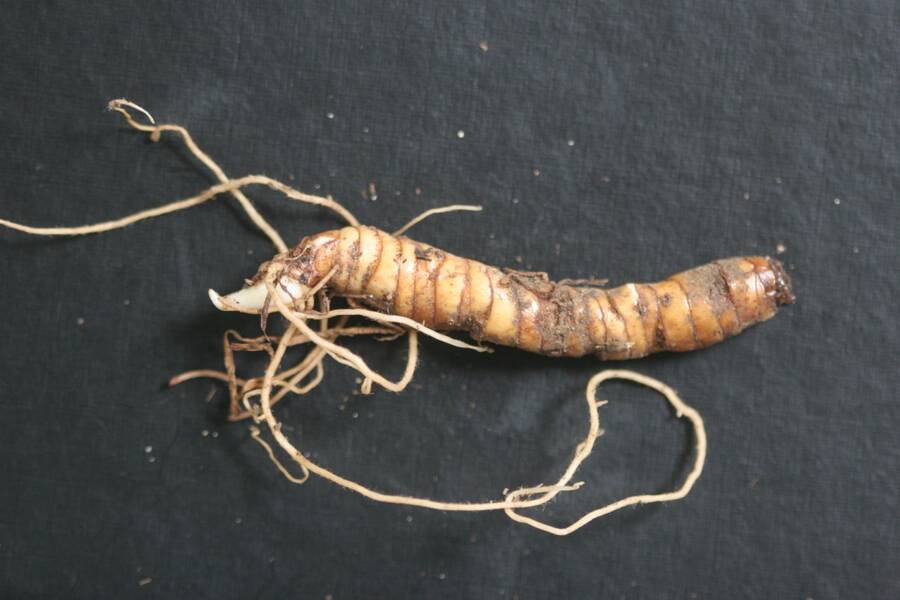
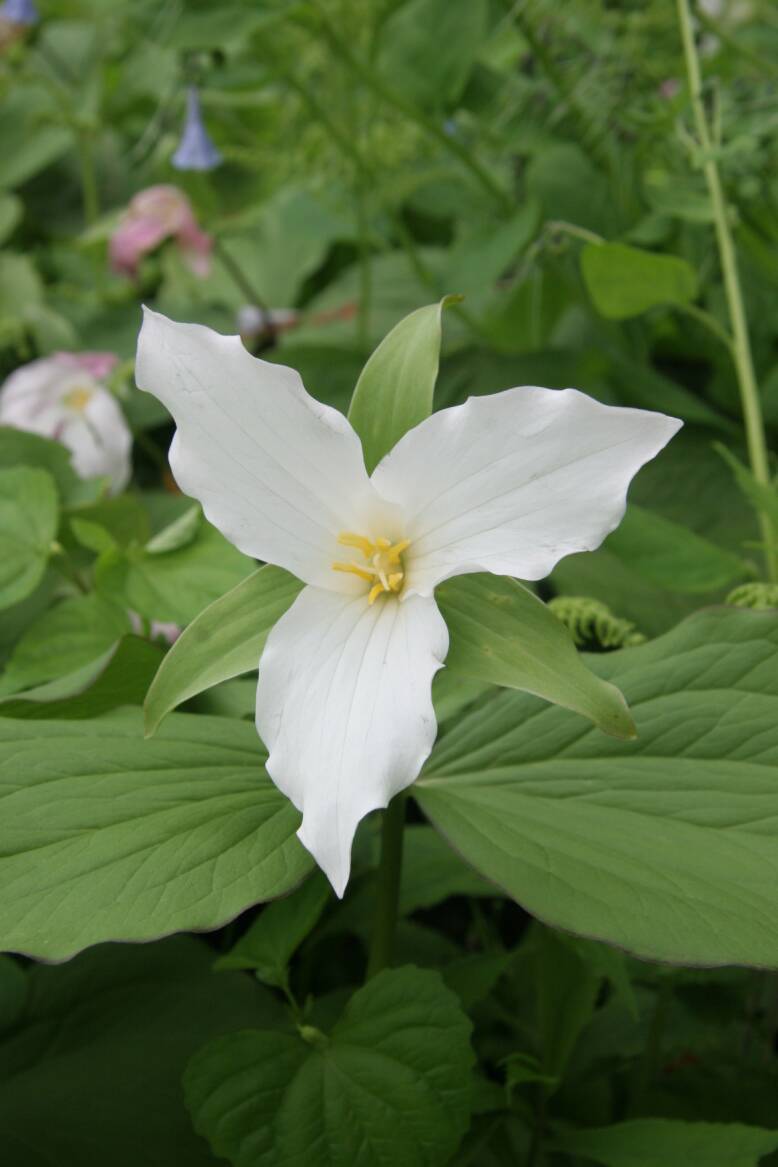


Tillium grandiflora
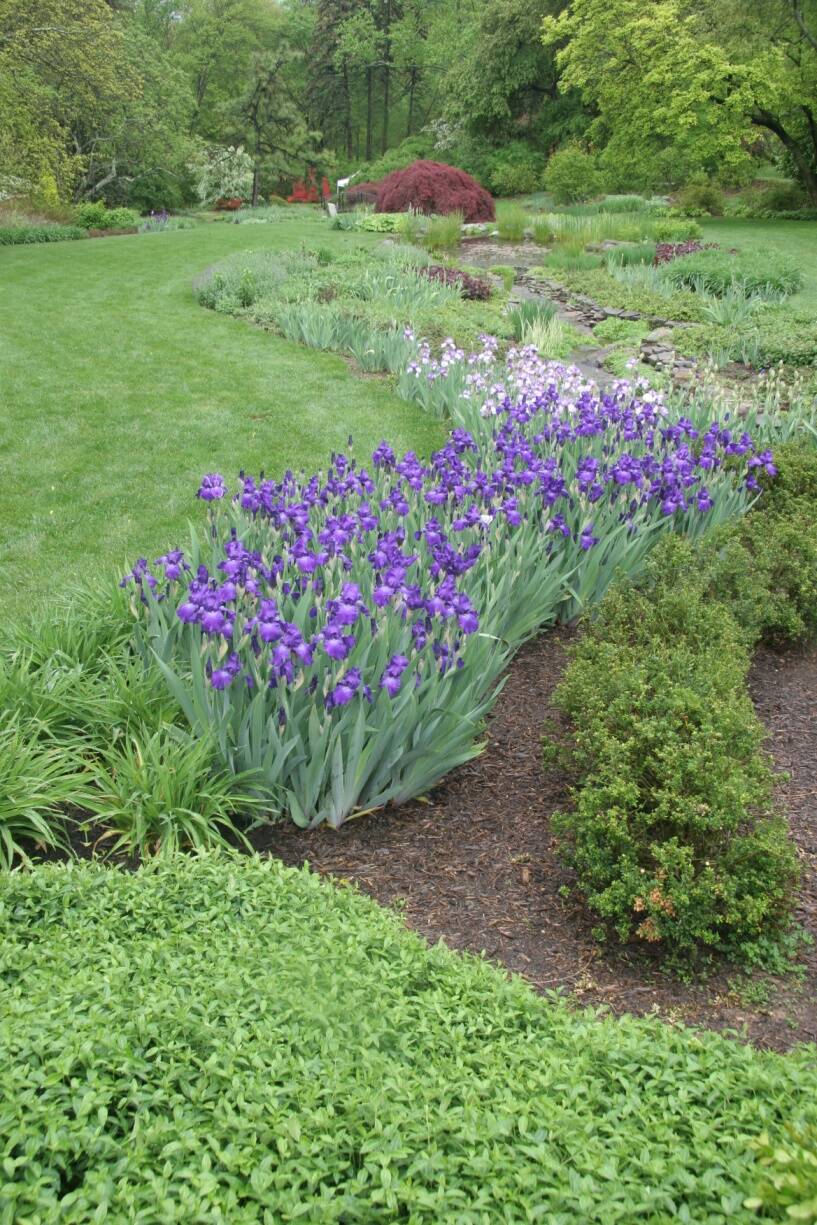
Plants with rhizomes are propagated by dividing the rhizome into sections containing vegetative buds.

Iris
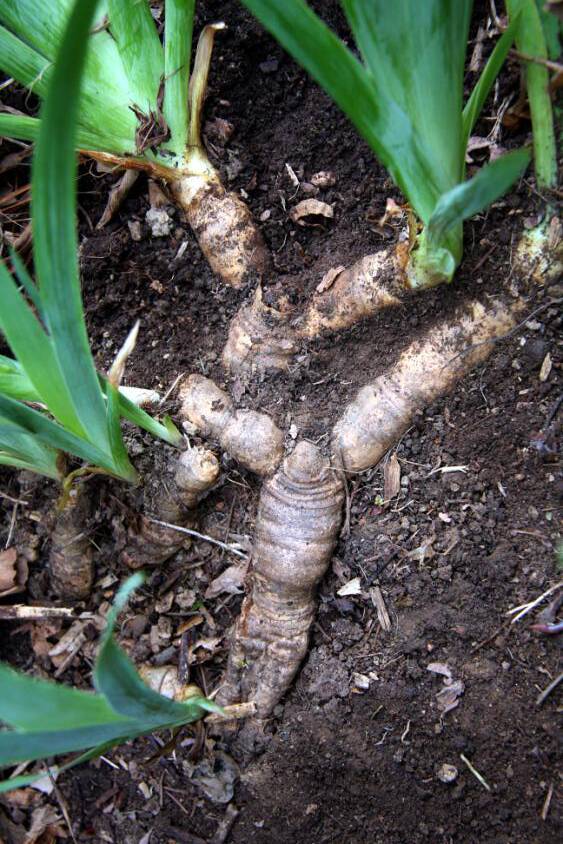

Iris


