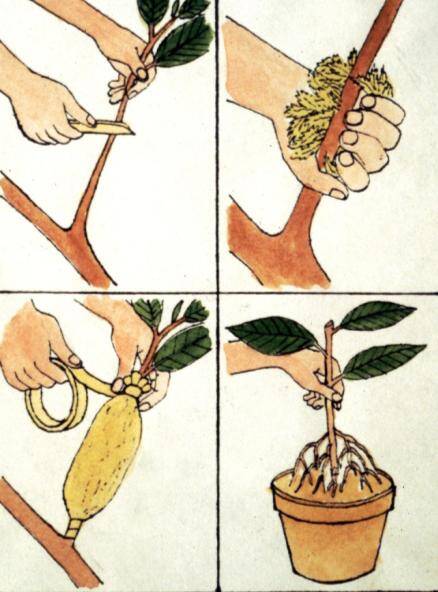
Air layering is an old method used to propagate plants.
It is useful for propagating a few plants of relatively large size for special purposes.
Some tropical trees that are difficult to root from cuttings are still propagated by this method.
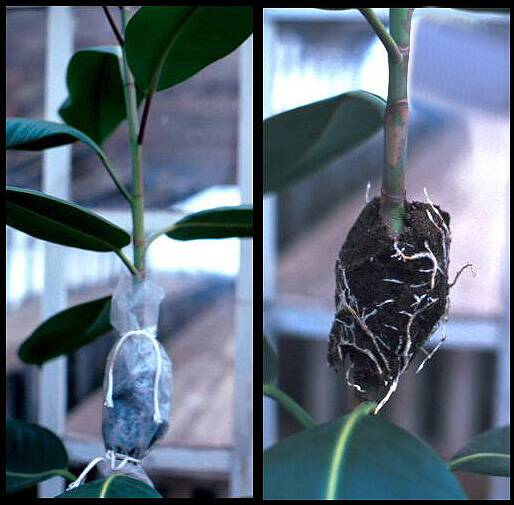

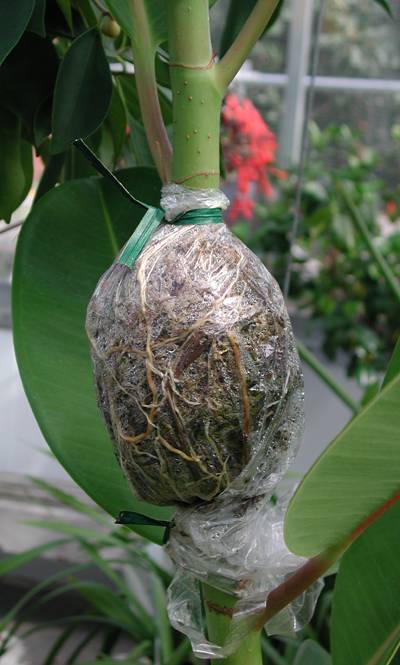
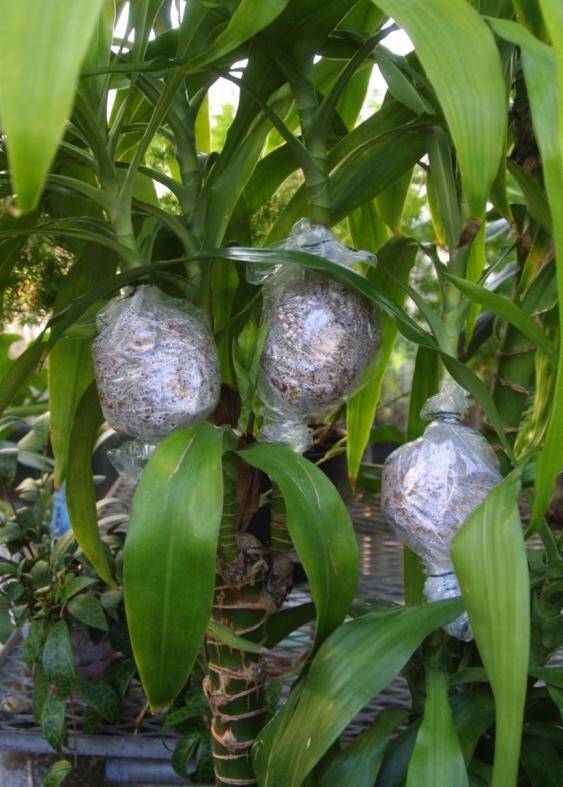
Steps for making an air layer include:
- Girdle stem.
- Remove several leaves around wound.
- Pack area with moist sphagnum or peat moss.
- Cover moss with polyethylene plastic and tie each end.
- Check to make sure moss remains moist until roots form.
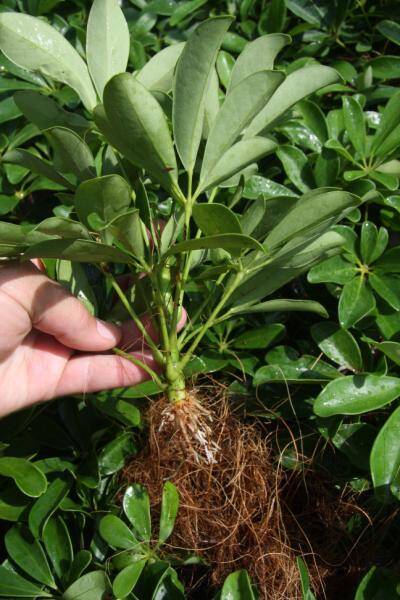
- After roots are visible inside the bag, the rooted stem can be cut from the mother plant and potted.
Reflective foil or black plastic may be used to protect the rooting area of the layer.
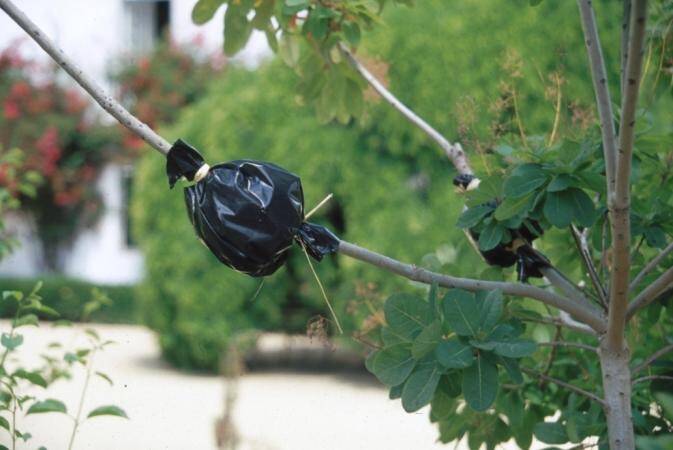


Air layers are usually made on stems from the previous season's growth. Best results are from shoots with several leaves on stems that are actively growing.


Because it can be so humid in the tropics, air layering can be successful by girdling the stem and covering with aluminum foil.
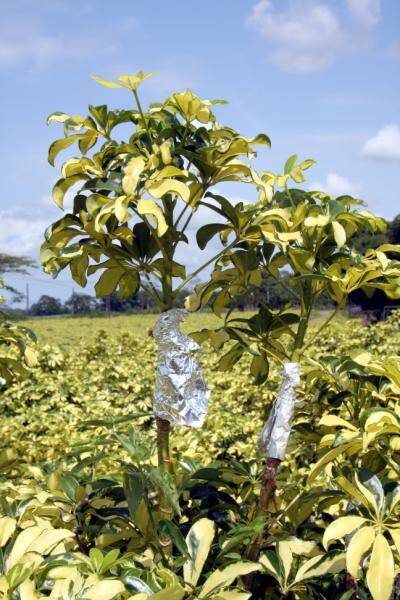
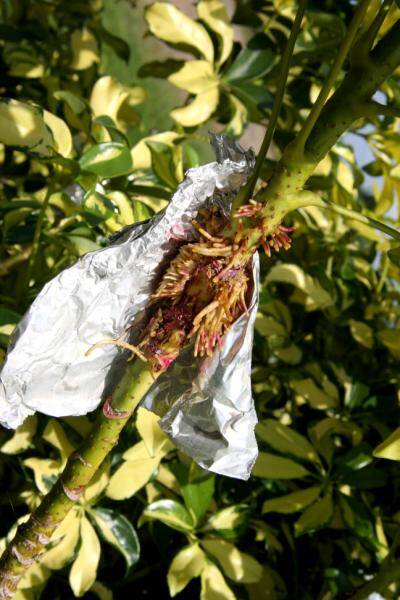


Schefflera (Brassaia)

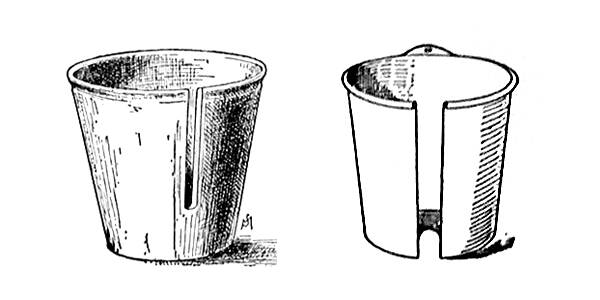
A variation of air layering uses specialized containers during layering.
This has been referred to as pot layering.
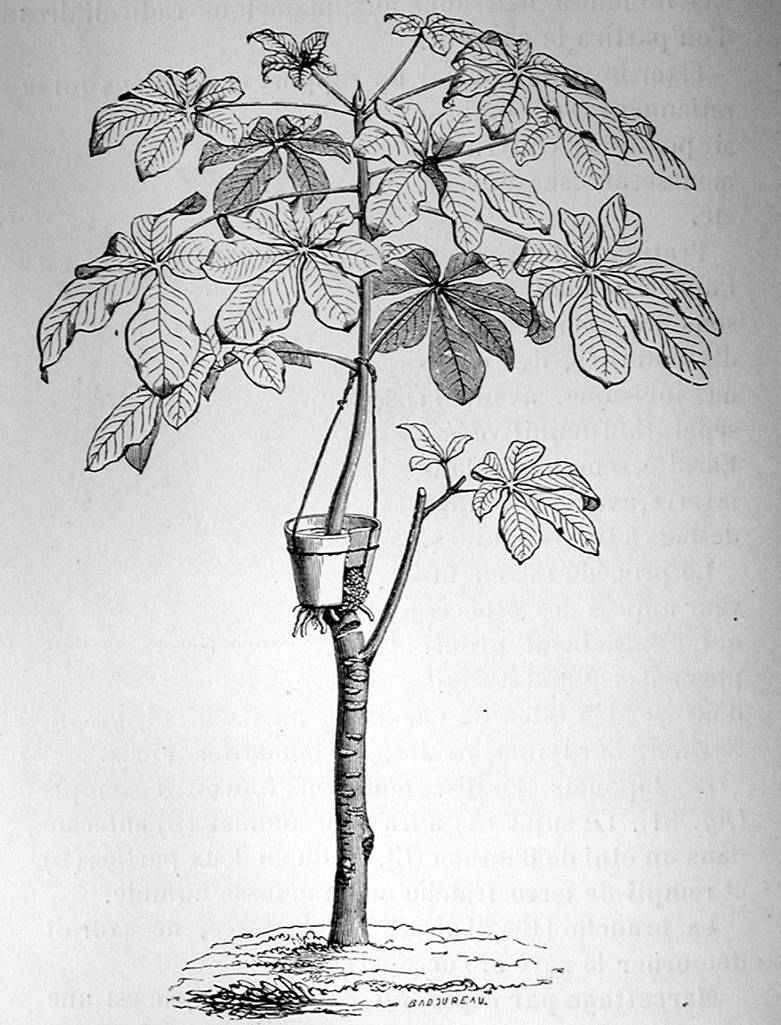


Charles Baltet 1903
Several types of containers have been designed for air layering.
These were split or open on one side to fit around the layered branch.
Liberty Hyde Bailey 1896


